User feedback is the cornerstone of product success. Yet, many companies struggle to collect meaningful feedback, analyze it effectively, and turn insights into action. This comprehensive guide will show you exactly how to build a user feedback system that drives real product improvements.
Why user feedback matters more than ever
In 2025, the competition for user attention has never been fiercer. Products that succeed are those that truly understand and respond to their users' needs. Industry research shows that companies that actively collect and act on user feedback typically see:
- Significantly higher customer retention rates compared to those that don't
- Faster time-to-market for new features by focusing on what users actually need
- Reduced development waste by avoiding features nobody uses
- Improved customer satisfaction scores across the board
The Challenge: Collecting feedback is easy. Collecting useful feedback that you can actually act on? That's an art and a science.
The 7 types of user feedback you need to collect
Not all feedback is created equal. To get a complete picture of your users' experience, you need to collect multiple types of feedback:
1. Feature requests
These tell you what users want next. Feature request feedback helps you prioritize your product roadmap based on actual user needs rather than assumptions.
Best for: Product planning, roadmap prioritization
Collection method: Dedicated feature request widgets, in-app voting systems
Frequency: Ongoing
2. Bug reports and issues
Users reporting problems are giving you a gift. They're invested enough to tell you when something's wrong instead of just leaving.
Best for: Quality assurance, technical debt management
Collection method: In-app feedback forms, support tickets
Frequency: Ongoing, real-time
3. User satisfaction surveys
Measure how happy users are with your product overall. This includes NPS (Net Promoter Score), CSAT (Customer Satisfaction Score), and CES (Customer Effort Score).
Best for: Tracking overall health, identifying trends
Collection method: Email surveys, in-app surveys
Frequency: Monthly or quarterly
4. Usability feedback
Understand how easy or difficult your product is to use. This type of feedback reveals friction points in your user experience.
Best for: UX improvements, onboarding optimization
Collection method: User testing sessions, screen recordings, heatmaps
Frequency: After major updates or for specific features
5. Feature-specific feedback
Gather opinions on specific features or recent changes. This helps you understand what's working and what needs improvement.
Best for: Feature validation, iteration
Collection method: Contextual surveys, thumbs up/down widgets
Frequency: After feature launches
6. Onboarding feedback
New users have fresh eyes and can spot confusing elements that power users no longer notice.
Best for: Improving first-time user experience
Collection method: Post-signup surveys, onboarding flow surveys
Frequency: Immediately after key onboarding milestones
7. Churn feedback
Understanding why users leave is crucial for retention. Exit interviews and cancellation surveys provide invaluable insights.
Best for: Retention improvements, identifying deal-breakers
Collection method: Cancellation surveys, exit interviews
Frequency: At the moment of cancellation or shortly after
How to choose the right feedback collection method
The method you choose significantly impacts the quality and quantity of feedback you receive. Here's how to match methods to your goals:
In-app surveys (typical response rate: 15-25%)
Best for: Active users, context-specific feedback
Pros: High response rates, contextual, timely
Cons: Can interrupt user flow if poorly timed
When to use: After specific user actions, during key moments in the user journey, for feature-specific feedback.
Email surveys (typical response rate: 5-10%)
Best for: Comprehensive feedback, periodic check-ins
Pros: Non-intrusive, can be longer
Cons: Lower response rates, delayed feedback
When to use: Monthly/quarterly satisfaction surveys, NPS campaigns, detailed customer research.
Embedded feedback widgets (typical response rate: 8-15%)
Best for: Passive feedback collection, always-available option
Pros: Always accessible, doesn't interrupt flow
Cons: May be overlooked, selection bias toward frustrated users
When to use: Continuous feedback collection, bug reporting, feature requests.
Note: Response rates vary significantly based on timing, audience engagement, question quality, and industry. These are general benchmarks to guide your expectations.
User interviews (Response rate: varies, highly targeted)
Best for: Deep insights, complex topics
Pros: Rich qualitative data, follow-up questions possible
Cons: Time-intensive, limited scale
When to use: Exploring new feature ideas, understanding complex workflows, persona development.
Live chat and support tickets (Passive collection)
Best for: Problem identification, feature requests
Pros: Natural, ongoing, detailed context
Cons: Unstructured, skewed toward problems
When to use: Always active for support, mine for patterns and trends.
The anatomy of a great feedback question
The quality of your questions directly determines the quality of feedback you receive. Here's how to write questions that get useful responses:
1. Be specific, not vague
Bad: "How was your experience?"
Good: "How easy was it to find the export button on the dashboard?"
Specific questions get actionable answers. Vague questions get vague responses.
2. Avoid leading questions
Bad: "Don't you love our new feature?"
Good: "What do you think of the new dashboard layout?"
Leading questions bias responses and give you false positives.
3. Use appropriate scale types
Different scales work for different questions:
- 1-5 scale: Quick, simple satisfaction measurements
- 1-10 scale: NPS, more granular feedback
- Likert scale: Agreement/disagreement statements
- Binary (Yes/No): Quick validation, simple choices
4. Keep it short
Survey completion rates decline significantly for surveys longer than 5 minutes. Ask only what you truly need to know.
5. Make rating labels clear
Bad: 1 to 5 with no labels
Good: 1 (Very Difficult) to 5 (Very Easy)
Clear labels prevent misinterpretation and ensure consistent responses.
When to ask for feedback (timing is everything)
The right question at the wrong time gets ignored. Here's when to trigger different types of feedback:
Immediately after key actions
- After completing onboarding
- After using a new feature for the first time
- After achieving a milestone in your product
Example: "How easy was it to set up your first survey?" (Try our interactive survey builder demo)
During moments of delight or frustration
- After a user completes a complex task successfully
- When a user attempts the same action multiple times (potential friction)
- When error messages appear
Example: "We noticed you tried to import contacts several times. What can we improve?"
At regular intervals
- 30 days after signup (onboarding complete)
- 90 days after signup (established user)
- Before renewal (annual plans)
Example: "How likely are you to recommend [Product Name] to a colleague?" (NPS survey)
Before they churn
- When engagement drops significantly
- When cancellation is initiated
- 30 days after last login
Example: "We noticed you haven't logged in recently. What can we do better?"
How to analyze feedback effectively
Collecting feedback is only half the battle. Here's how to turn raw feedback into actionable insights:
1. Categorize and tag feedback
Create a consistent tagging system:
- Feature category (e.g., "Dashboard", "Reports", "Settings")
- Feedback type (e.g., "Bug", "Feature Request", "Usability")
- Sentiment (Positive, Neutral, Negative)
- Priority (High, Medium, Low)
2. Look for patterns, not individual requests
One person asking for a feature might be an outlier. 50 people asking for the same thing? That's a pattern worth exploring.
3. Consider the source
Weight feedback based on:
- User tenure (new vs. power users)
- Account value (free vs. paid tiers)
- Usage frequency (active vs. occasional users)
- Industry or use case
4. Track metrics over time
Monitor trends in:
- NPS scores
- Feature request votes
- Bug report frequency
- Satisfaction ratings by feature
5. Close the loop
Always follow up with users who provided feedback:
- Thank them for their input
- Let them know when you've implemented their suggestion
- Explain why you can't implement certain requests
Common feedback collection mistakes (and how to avoid them)
Mistake #1: Asking for feedback too often
The problem: Survey fatigue leads to declining response rates and annoyed users.
The fix: Set a maximum survey frequency (e.g., no more than once per month per user). Respect user preferences if they decline to participate.
Mistake #2: Not acting on feedback
The problem: Users stop providing feedback when they see nothing changes.
The fix: Publicly share what you've changed based on feedback. Create a feedback changelog or "You asked, we built" section.
Mistake #3: Only listening to vocal users
The problem: The loudest users don't always represent your broader user base.
The fix: Actively reach out to silent users. Analyze usage data alongside feedback to get the complete picture.
Mistake #4: Making surveys too long
The problem: Long surveys have low completion rates and tired respondents give poor quality answers.
The fix: Keep surveys under 5 minutes. Ask only essential questions. Use progressive disclosure for optional follow-ups.
Mistake #5: Ignoring negative feedback
The problem: Negative feedback is uncomfortable, but it's often the most valuable.
The fix: Treat critical feedback as a gift. These users care enough to help you improve instead of just leaving.
Building a sustainable feedback loop
A one-time feedback collection effort won't transform your product. You need a systematic approach:
Phase 1: Collect (Weekly)
- Set up automated feedback triggers
- Monitor support tickets and chat logs
- Review feature request submissions
- Check social media mentions
Phase 2: Analyze (Weekly)
- Categorize new feedback
- Identify emerging patterns
- Calculate key metrics (NPS, CSAT, etc.)
- Flag critical issues
Phase 3: Prioritize (Bi-weekly)
- Rank feedback by impact and effort
- Align with product roadmap
- Create action items for high-priority issues
- Assign owners to each item
Phase 4: Act (Monthly)
- Implement changes based on feedback
- Fix reported bugs
- Build requested features
- Improve pain points
Phase 5: Close the loop (Ongoing)
- Notify users when their feedback is implemented
- Share product updates highlighting user-driven changes
- Thank contributors publicly (with permission)
- Measure impact of changes
Tools and technology for feedback collection
The right tools make feedback collection effortless. Here's what you need:
Survey and form platforms
Look for tools that offer:
- Multiple question types (rating, multiple choice, text, etc.)
- Skip logic and branching
- Mobile optimization
- Analytics and reporting
- Integration with your product
Example: Ask Users provides embeddable surveys, forms, and feedback widgets designed specifically for product teams.
Feature request management
- Voting systems to prioritize requests
- Public roadmaps for transparency
- Status updates for submitted ideas
- Search to prevent duplicates
Try: Our feature request widget makes it easy for users to submit and vote on ideas.
Analytics platforms
- User behavior tracking
- Session recordings
- Heatmaps
- Funnel analysis
Customer support tools
- Ticket management
- Live chat
- Knowledge base with feedback options
- Sentiment analysis
Measuring the impact of your feedback program
How do you know if your feedback efforts are working? Track these metrics:
Collection metrics
- Response rate: % of users who provide feedback when asked
- Feedback volume: Total pieces of feedback collected
- Channel distribution: Where feedback comes from (in-app, email, etc.)
Benchmark: Aim for 15-20% response rate for in-app surveys (varies by audience)
Quality metrics
- Actionability rate: % of feedback that leads to action
- Specificity score: How detailed and useful feedback is
- Time to resolution: How quickly you address feedback
Benchmark: Strong feedback programs see 40%+ actionable feedback
Impact metrics
- NPS trend: Is your Net Promoter Score improving?
- Feature adoption: Are user-requested features actually used?
- Retention improvement: Does acting on feedback reduce churn?
- Development efficiency: Are you building the right things?
Goal: Positive trends across all metrics quarter-over-quarter
Advanced feedback collection strategies
Once you've mastered the basics, try these advanced techniques:
1. Cohort-based feedback
Segment users by signup date and track how feedback evolves as cohorts mature. This reveals whether issues are permanent or part of the learning curve.
2. Sentiment analysis at scale
Use AI to automatically categorize and score feedback sentiment. This helps you quickly identify urgent issues from thousands of responses.
3. Feedback prediction
Use behavioral data to predict which users are likely to provide valuable feedback and prioritize reaching out to them.
4. Multi-channel triangulation
Combine feedback from surveys, support tickets, analytics, and user testing to get a complete picture. Different channels reveal different insights.
5. Competitive feedback
Ask users what they like about competing products. This reveals gaps in your offering and opportunities for differentiation.
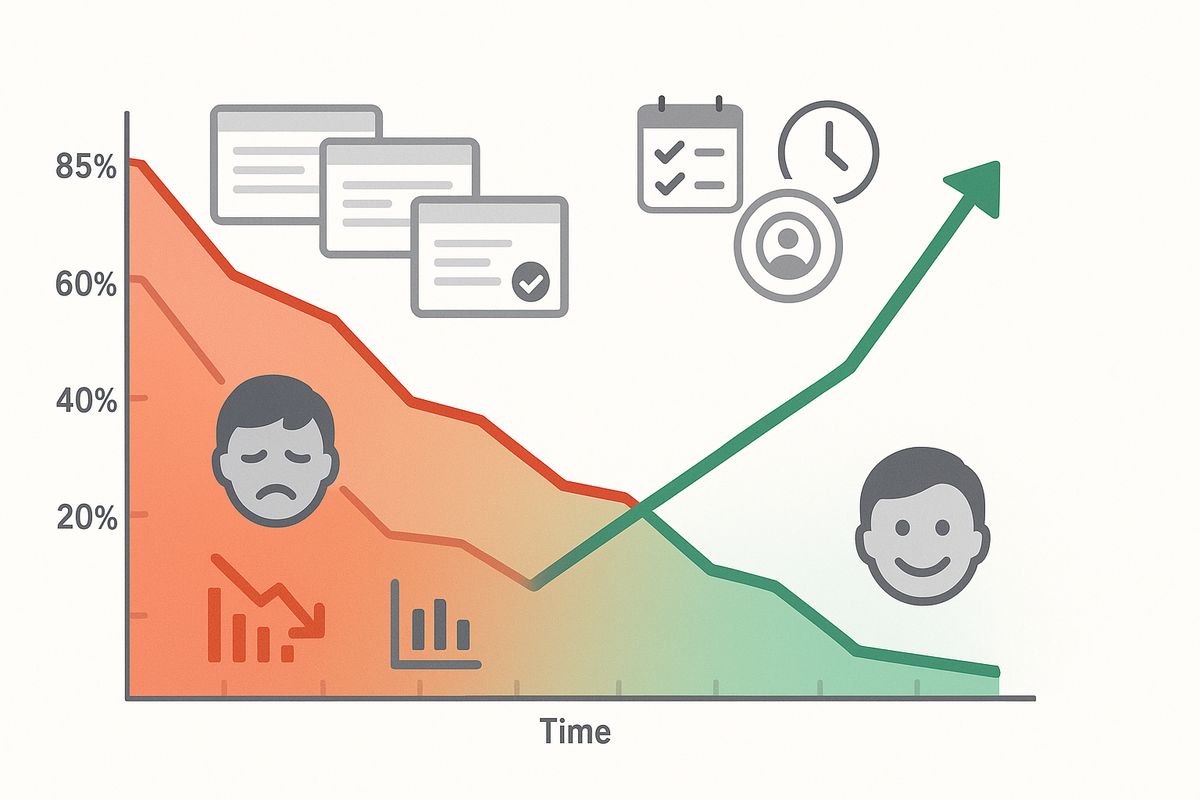
Real-world example: How feedback can transform a SaaS product
Consider a typical scenario: A project management tool struggling with high churn implements a comprehensive feedback program:
- Added exit surveys to understand why users left
- Discovered 67% of churners mentioned difficulty with team collaboration features
- Conducted 20 user interviews with active and churned users
- Redesigned collaboration features based on specific feedback
- Followed up with churned users to offer re-onboarding
Results after 6 months:
- Churn reduced from 8% to 4.2%
- NPS increased from 32 to 54
- Feature adoption up 156%
- 15% of churned users reactivated their accounts
Your action plan: Getting started today
Ready to build your feedback collection system? Follow this 30-day plan:
Week 1: Foundation
- Audit existing feedback channels
- Choose a primary feedback collection tool
- Define key metrics you want to track
- Create a feedback categorization system
Week 2: Implementation
- Set up in-app feedback widget
- Create your first 3 surveys (NPS, feature satisfaction, onboarding)
- Configure automated triggers
- Train your team on the new process
Week 3: Launch
- Start collecting feedback from 20% of users (A/B test)
- Monitor response rates and adjust timing
- Begin categorizing feedback
- Share first insights with the team
Week 4: Optimization
- Analyze first batch of feedback
- Identify top 3 actionable insights
- Create plan to address feedback
- Roll out to 100% of users
Final thoughts
User feedback isn't just data—it's a conversation with the people who determine your product's success. The companies that win are those that listen carefully, analyze thoughtfully, and act decisively on what their users tell them.
The difference between a good product and a great product often comes down to how well you understand and respond to user needs. Build feedback collection into your product DNA, and you'll build something people truly love.
Ready to put these strategies into action?
Ask Users makes it easy to collect, analyze, and act on user feedback. Create your first survey in minutes—no credit card required.
Frequently asked questions
How often should I ask users for feedback?
No more than once per month for general surveys. Feature-specific or contextual feedback can be more frequent but should be highly relevant to the user's current action.
What's a good survey response rate?
In-app surveys typically see 15-25% response rates. Email surveys are lower at 5-10%. Response rates vary by industry and audience, so focus on improving your own baseline over time. If you're below these benchmarks, consider improving your survey timing, length, or question quality.
Should I offer incentives for feedback?
Generally, no. Incentives can bias responses and attract users who aren't genuinely invested. However, for long research studies or user testing sessions, compensation for time is appropriate.
How do I handle negative feedback?
Thank the user, acknowledge their frustration, and explain what you're doing to address it. Even if you can't fix the issue immediately, showing you care makes a huge difference.
What's the ideal survey length?
Keep surveys under 5 minutes (about 8-10 questions). For quick pulse checks, 1-3 questions is even better.
Should surveys be anonymous?
Offer both options when possible. Anonymous surveys often get more honest (especially negative) feedback, but identified surveys allow for follow-up conversations.
Next steps
Ready to start collecting better feedback? Here are some helpful resources:
- Try our interactive survey builder demo - No signup required
- See real-world examples - Get inspired by successful feedback campaigns
- View pricing plans - Start with our free plan, upgrade when you're ready
- Explore survey widgets - See all the ways you can collect feedback